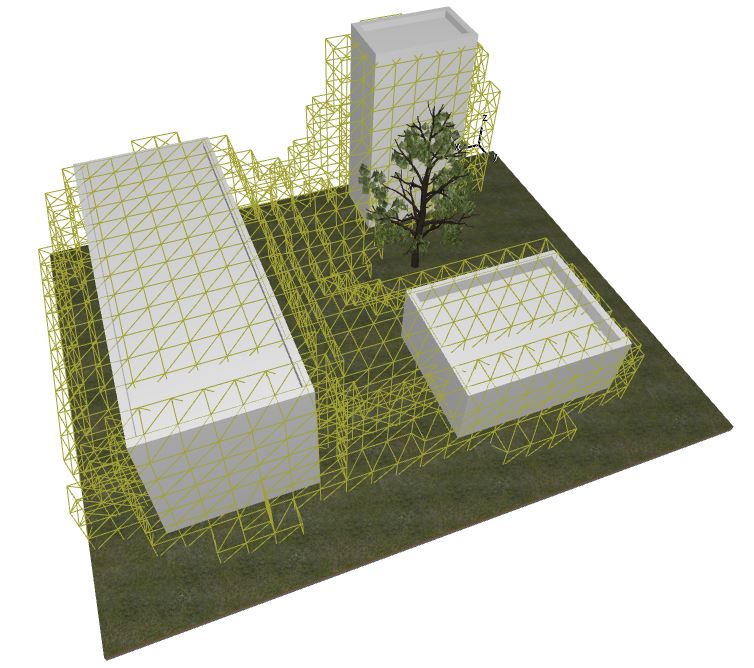
Shadow 3D analysis for BIM

If you have a building site and you wonder where do you want to plant trees given that certain kind of trees have specific sunlight requirements it may be a difficult task to determine the areas where it’ll be beneficial.

Most BIM software have the capability to set-up the sun based on the location of the project in the world, orientation to North and date+time.
In this case, Archicad is used which has the above-mentioned control, however each time there’s a change the shadows of the context are altered and it’s difficult to track down those changes. Especially the shadow is not a geometric object that we can play with and it’s not 3 dimensional.
Using the Archicad-Grasshopper live connection the context is transferred to Grasshopper where Ladybug can set the environment and analyse the shadow in the given context.
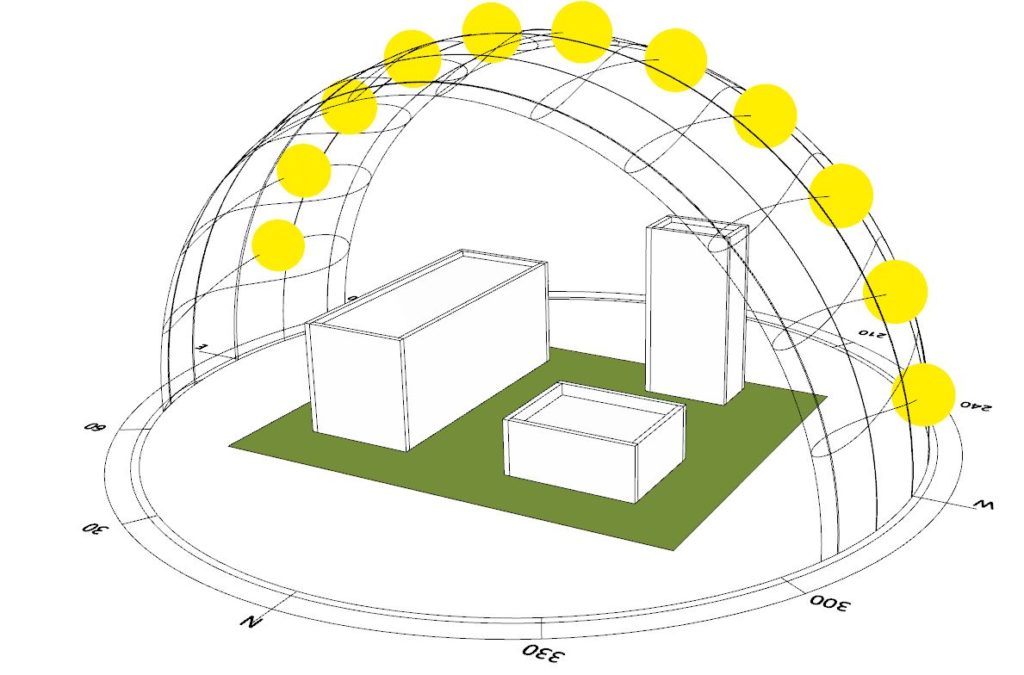
By inserting the location and analysis time period we can get the sun paths and ray vectors. In the given example the period is set to the entire year.
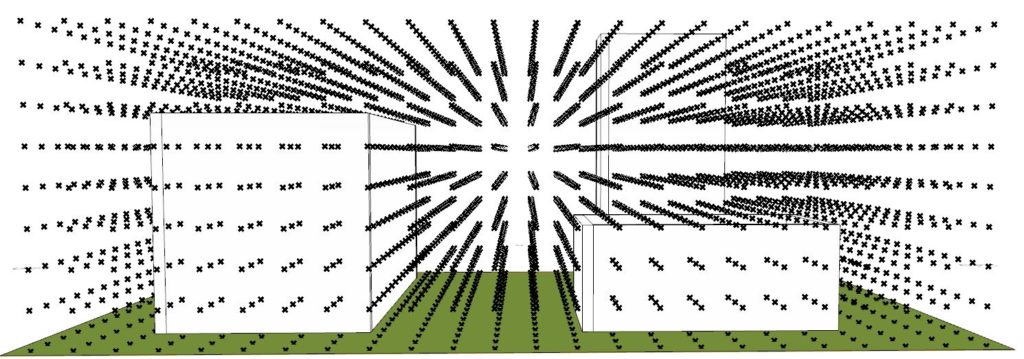
Next thing, the measurement sensor points are generated in the 3D grid space that will measure if the given area in space is receiving sunlight at every given hour or not.
The buildings that come from Archicad are set to be a context that can cast shadows.
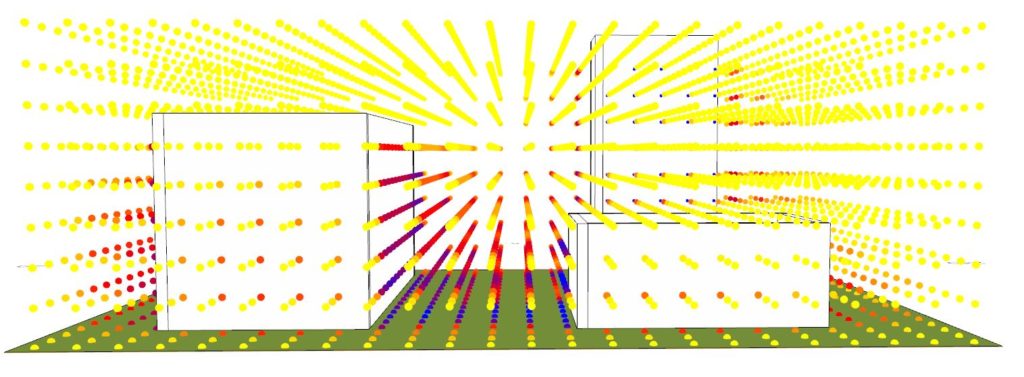

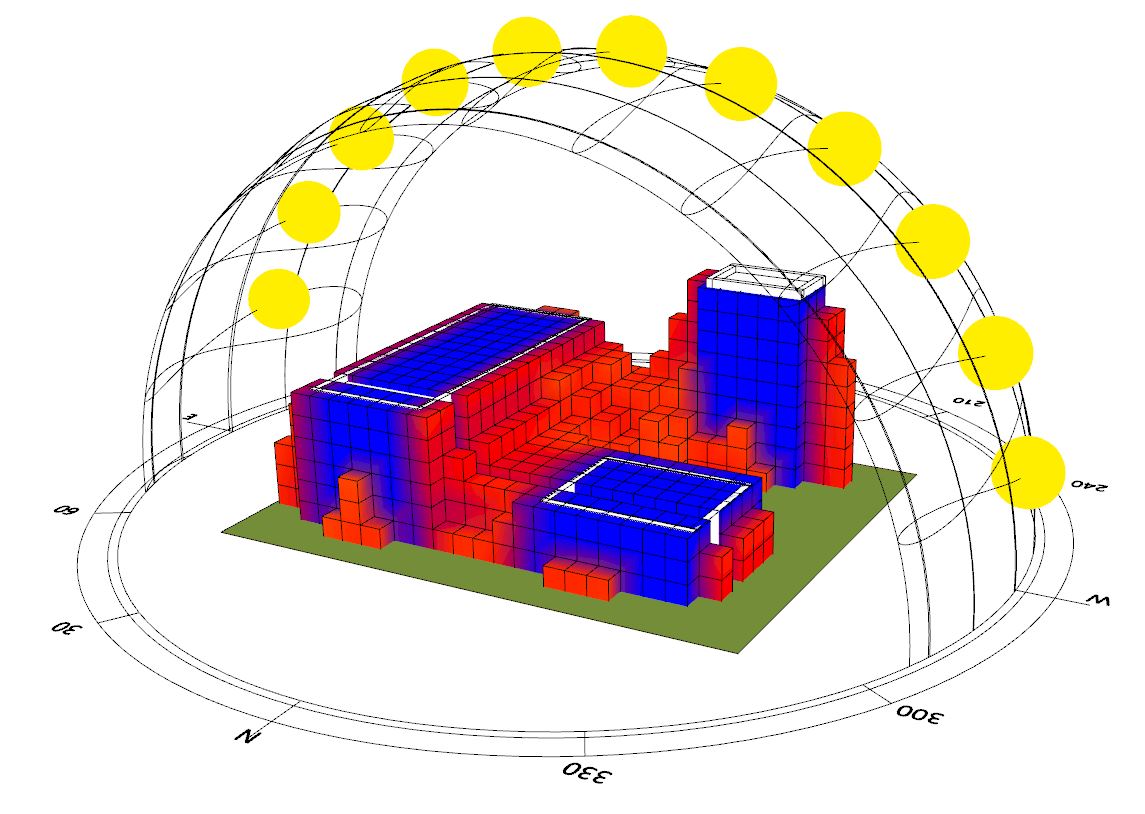
Having defined the lower and upper bounds for the analysis we can now calculate the total amount of sunlight for each measurement point in space. The higher the density of the points the higher will be computation time. This one took several minutes.
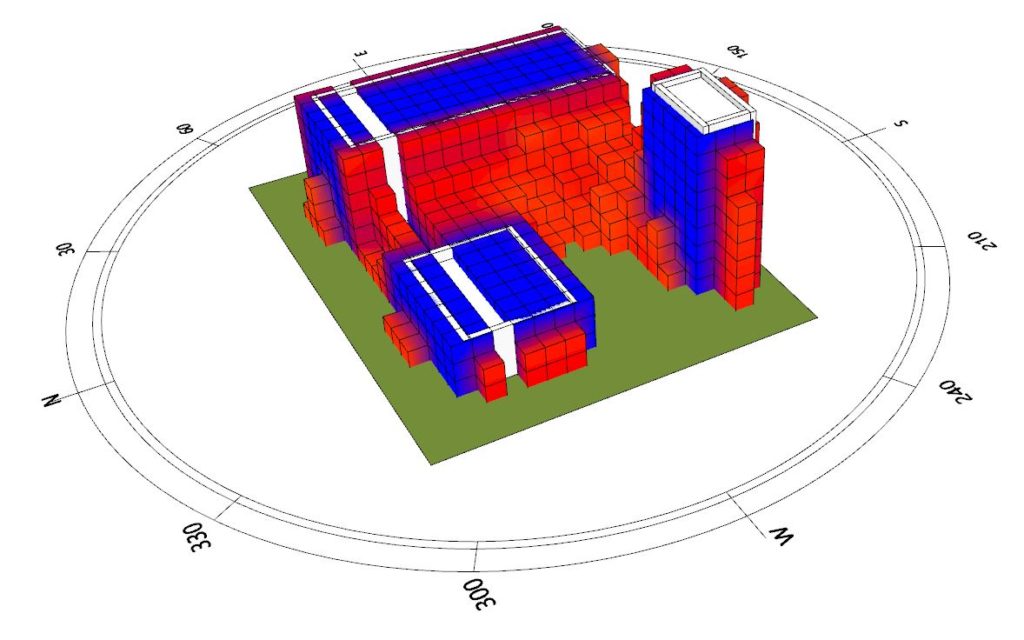
Having the information for each point we can select the part of 3D space that does not receive enough (given the threshold) sunlight and create a voxelised mesh to serve as a preventive boundary. The Voxelized mesh is created with Volvox.
Once we have the voxelised boundary of where we don’t want to place the trees we can transfer this mesh into Archicad so the user can make informed decision there.
